Earlier this year Stephen Collins and Chris Saad had flown to Sydney for the Future of Media summit, and in front of me were having heated discussions on how come nobody invited them to the Social Media club in Australia. As they were yapping away, I thought to myself what the hell are they going on about. It turns out things I used to call "blogs", "comments" or "wikis" were now "social media". Flickr, Delicious, YouTube? No longer Web 2.0 innovations, but social media. Bulletin boards that you would dial up on your 14000 kbps modem? Social media. Online forums discussing fetishes? Social media. Everything was now bloody social media (or Social Media: tools are lower case, concept uppercase) and along with Dare Obasanjo I was asleep for the two hours when it suddenly happened.
However it turns out that this is a term that’s been around for a lot longer than we give it credit for. It hung low for a while and then as some significant events occurred this year the term became a perfect fit to describe what was happening. It’s a term that I’ve been waiting to emerge for years now, as I knew the term "new media" was going to mature one day.
Ladies and gentlemen, welcome to our new world and the way of defining it: 2008 is when the Information Age’s "social media" finally displaced the Industrial Era’s "mass media". Below I document how, when and why.
Origins of the term and its evolution
The executive producer of the Demo conference Chris Shipley is said to have coined the term during a key note at the Demofall 2005 conference on the 20th September 2005. As she said in her speech:
Ironically, perhaps, there is one other trend that would at first blush seem at odds with this movement toward individuality, and that is the counter movement toward sociability.
As one reporter pointed out to me the other day, the program book you have before you uses the term “social” a half-dozen times or more to describe software, computing, applications, networks and media.
I’m not surprised that as individuals are empowered by their communications and information environments, that we leverage that power to reach out to other people. In fact, blogs are as much about individual voice as they are about a community of readers.
The term gained greater currency over the next year, as Shipley would use the term in her work and various influencers like Steve Rubel would popularise the term. Brainjam which popularised unConferences first had the idea of a Social Media Club around the time of Shipley’s keynote and eventually formed it in July of the following year, which created more energy towards pushing for the term. Other people starting building awareness, like the Hotwire consultant Drew Benvie who from April 2006 has been writing the Social Media Report (and created the Social media Wikipedia page on 9 July 2006). Benvie said to me in some private correspondence: “When social media emerged as a category of the media landscape in 2005 / 2006 I noticed the PR and media industries looking for suitable names. The term social media came to be used at the same time of social networks becoming mainstream.” Back then it was more a marketing word to conceptualise online tools and strategies to deal with them, which is why there has been distaste for the term that prevented its adoption.
It was 2008 however when several news incidents, innovations, and an election entrenched this term into our consciousness. Later on, I will explain that, but first a lesson.
So what is Social Media?
A debate in August 2008 created the following definition: "social media are primarily Internet and mobile-based tools for sharing and discussing information among human beings. " I like that definition, but with it, you could arguably say "social media" existed when the first e-mail was sent in the 1970s. Perhaps it’s going to suffer the fate of the term “globalisation” where in the 1990s people didn’t know the term existed – but by 2001 in high school, I was told it had been around since the 1980s and by my final year of university in 2004 I was told "globalisation" started in the 1700s. Heaven forbid it turns into a term like "Web 2.0" where no one agrees but it somehow becomes a blanket term for everything that is post the Dot-Com bubble.
The definition is off-putting unless you have a fundamental understanding of what exactly media is. It might shock you to hear this, but a newspaper and a blog are not media. A television and a Twitter account, are not media either. So if you’ve had had trouble getting the term social media before, it’s probably because you’ve been looking at it in the wrong way. Understand what media really is and you will recognise the brilliance of the term "social media".
Vin Crosbie many years ago answered a question I had been searching half a decade ago on what was new media. Crosbie’s much cited work has moved around the Internet, so I can’t link to his original piece of work (update: found it on the Internet archive), but this is what he argued in summary.
- Television, books and websites are wrongly classified as media. What they really are, are media outputs. We are defining our world on the technology, and not the process. Media is about communication of messages.
- There are three types of media in the world: Interpersonal media, mass media, and new media.
- Interpersonal media, which he coined for lack of an established term, is a one-on-one communications process. A person talking directly to another person is interpersonal media. It’s one message distributed to one other person, from one person.
- Mass media is a one-to-many process. That means, one entity or person is communicating that one message to multiple people. So if you are standing in front of a crowd giving a speech, you are conducting a mass media act. Likewise, a book is mass media as it’s one message distributed to many
- New media, which is only possible due to the Internet, is many-to-many media.
I highly recommend you read his more recent analysis which is an update of his 1998 essay (can be seen here on the Internet archive ).
That’s a brilliant way of breaking it down but I still didn’t get what many-to-many meant. When the blogosphere tried to define social media it was a poor attempt (and as recently as November 2008, it still sucked). But hidden in the archives of the web, we can read Stowe Boyd who came up with the most accurate analysis I’ve seen yet.
- Social Media Is Not A Broadcast Medium: unlike traditional publishing — either online or off — social media are not organized around a one-to-many communications model.
- Social Media Is Many-To-Many: All social media experiments worthy of the name are conversational, and involve an open-ended discussion between author(s) and other participants, who may range from very active to relatively passive in their involvement. However, the sense of a discussion among a group of interested participants is quite distinct from the broadcast feel of the New York Times, CNN, or a corporate website circa 1995. Likewise, the cross linking that happens in the blogosphere is quite unlike what happens in conventional media.
- Social Media Is Open: The barriers to becoming a web publisher are amazingly low, and therefore anyone can become a publisher. And if you have something worth listening to, you can attract a large community of likeminded people who will join in the conversation you are having. [Although it is just as interesting in principle to converse with a small group of likeminded people. Social media doesn’t need to scale up to large communities to be viable or productive. The long tail is at work here.]
- Social Media Is Disruptive: The-people-formerly-known-as-the-audience (thank you, Jay Rosen!) are rapidly migrating away from the old-school mainstream media, away from the centrally controlled and managed model of broadcast media. They are crafting new connections between themselves, out at the edge, and are increasingly ignoring the metered and manipulated messages that centroid organizations — large media companies, multi national organizations, national governments — are pushing at them. We, the edglings, are having a conversation amongst ourselves, now; and if CNN, CEOs, or the presidential candidates want to participate they will have to put down the megaphone and sit down at the cracker barrel to have a chat. Now that millions are gathering their principal intelligence about the world and their place in it from the web, everything is going to change. And for the better.
So many-to-many is a whole lot of conversation? As it turns out, yes it is. Now you’re ready to find out how 2008 became the year Social Media came to maturity.
How 2008 gave the long overdue recognition that New Media is Social Media
The tools: enabling group conversations
MySpace’s legacy on the world is something that I think is under-recognised, that being the ability to post on peoples’ profiles. It gave people an insight into public communication amongst friends, as people used it more for open messaging rather than adding credentials like the feature originally intended when developed on Friendster. Yes, I recognise public discussions have occurred for years on things like forums and blogs, but this curious aspect of MySpace’s culture at its peak has a lot to answer for what is ultimately Social Media. Facebook picked up on this feature and more appropriately renamed it as "wall posts" and with the launch of the home screen that is essentially an activity stream of your friends, it created a new form of group communication.
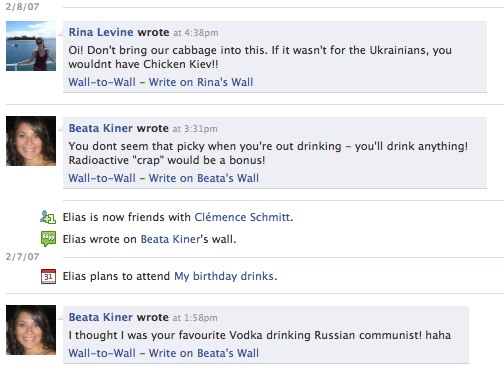
The image below shows a wall-to-wall conversation with a friend of mine in February 2007 on Facebook. You can’t see it, but I wrote a cheeky response to Beata’s first message at the bottom about her being a Cabbage-eating Ukrainian communist whose vodka is radioactive from Chernobyl. She responds as you can see, but more interestingly, our mutual friend Rina saw the conversation on her homescreen and jumped in. This is a subtle example that shows how the mainstream non-technology community is using social media. I’m currently seeing how non-technology friends of mine will share links that appear on the activity stream and how they jump into a conversation about it right there. It’s like over-hearing a conversation around the water-cooler and joining in if you want.
This is what made Twitter what it is. What started as a status update tool for friends, turned into a chat-room with your friends; you can see the messages posted by people you are mutually following, and you can join in on a conversation that you weren’t originally a part of. Again, simple but the impact we have seen it have on the technology community is unbelievable. Like for example, I noticed Gabe Rivera a few days ago had a discussion with people about how he still doesn’t get what social media is. I wasn’t involved in that discussion originally, but its resulted in me partially inspired to explore the issue with this blog post. These are subtle, anecdotal examples but in sum they point to this broader transformation occurring in our society due to these tools that allow us to mass collaborate and communicate. The open conversation culture of Web 2.0 has helped create this phenomenon.
Another Internet start-up company which I think has contributed immensely to the evolution of Social Media is Friendfeed. It essentially copied the Facebook activity screen, but made it better – and in the process, created the closest thing to a social media powerhouse. People share links there constantly and get into discussions in line. In the mass media, an editor would determine what you could read in a publication; in the Social Media world, you determine what you read based on the friends you want to receive information from. Collectively, we decimate information and inform each other: it’s decentralised media. Robert Scoble, a blogging and video super star, is the central node of the technology industry. He consumes and produces more information than anyone else in this world; and if he is spending seven days a week for seven hours a day on Friendfeed, that’s got to tell you something’s up.
The events: what made these tools come to life in 2008
We’ve often heard about citizen journalism with people posting pictures from their mobile phones to share with the broader Internet. Blogs have long been considered a mainstay in politics this last decade. But it was 2008 that saw two big events that validated Social Media’s impact and maturity.
- A new president: Barack Obama has been dubbed as the world’s first Social Media president. Thanks to an innovative use of technology (and the fact one of the co-founders of Facebook ran his technology team – 2008 is the year for Social Media due to cross pollination), we’ve seen the most powerful man in the world get elected thanks to the use of the Internet in a specific way. Obama would post on Twitter where he was speaking; used Facebook in a record way; posted videos on YouTube (and is doing a weekly video addresses now as president-elect) – and a dozen other things, including his own custom-built social networking site.
- A new view of the news: In November, we saw a revolting event occur which was the terrorist situation in India (and which has now put us on the path of a geopolitical nightmare in the region). However the tragic event at Mumbai, also gave tangible proof of the impact social media is having in the world .
What’s significant about the above two events is that Social Media has robbed the role played by the Mass Media in the last century and beyond. Presidents of the past courted newspapers, radio and television personalities to get positive press as Mass Media influenced public perception. Likewise, breaking news has been the domain of the internationally-resourced Mass Media. Social Media is a different but much better model.
What’s next?
It’s said we need bubbles as they fuel over-development that leave something behind forever. The last over-hyped Web 2.0 era has given us a positive externality that has laid the basis of the many-to-many communications required for New Media to occur. Arguably, the culture of public sharing that first became big with the social bookmarking site Del.icio.us sparked this cultural wave that has come to define the era. The social networking sites created an infrastructure for us to communicate with people en masse, and to recognise the value of public discussions. Tools like wikis both in the public and the enterprise have made us realise the power of group collaboration – indeed, the biggest impact a wiki has in a corporation from my own experience rolling out social media technologies at my firm, is encouraging this culture of "open".
It has taken a long time to get to this point. The technologies have taken time to evolve (ie, connectivity and a more interactive experience than the document web); our cultures and societies have also needed some time to catch up with this massive transformation in our society. Now that the infrastructure is there, we are busy concerning ourselves with refining the social model. Certainly, the DataPortability Project has a relevant role in ensuring the future of our media is safe, like for example the monitoring the Open Standards we use to allow people to resuse their data. If my social graph is what filters my world, then my ability to access and control that graph is the equivalent to the Mass Media’s cry of ensuring freedom of the press.
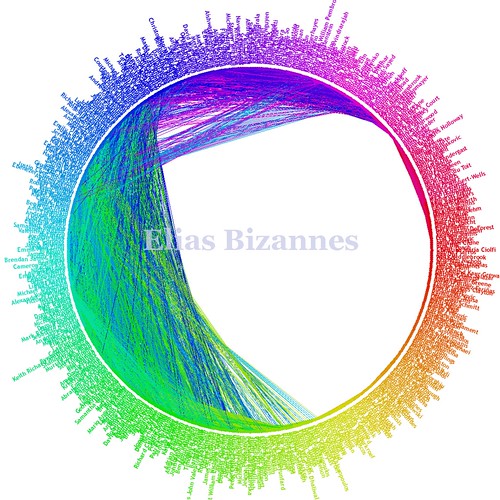
Over 700 people in my life – school friends, university contacts, workmates and the rest – are people I am willing to trust to filter my information consumption. It will be key for us to be able to control this graph
Newspapers may be going bankrupt thanks to the Internet, but finally in 2008, we now can confidently identify the prophecies of what the future of media looks like.